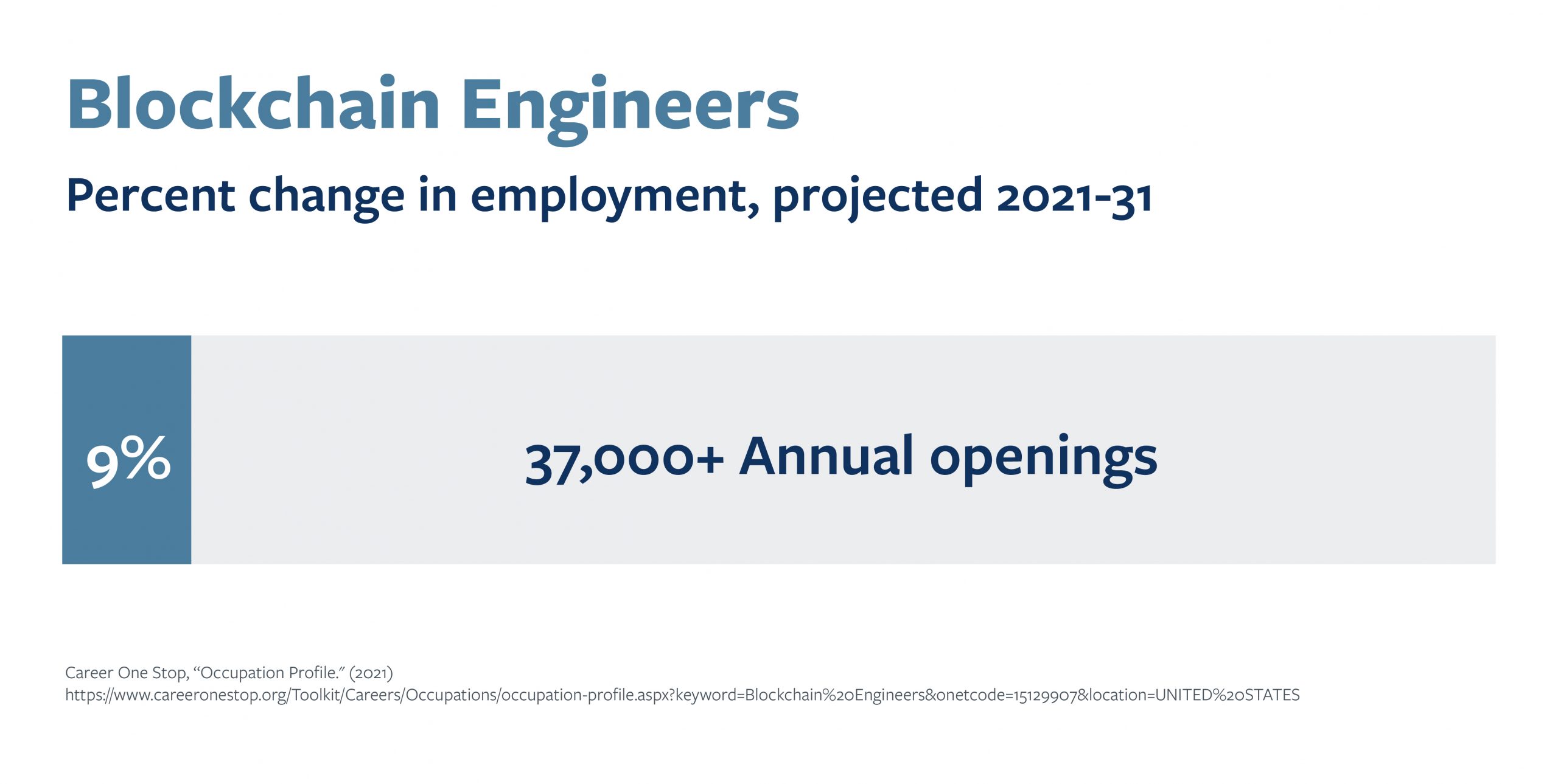
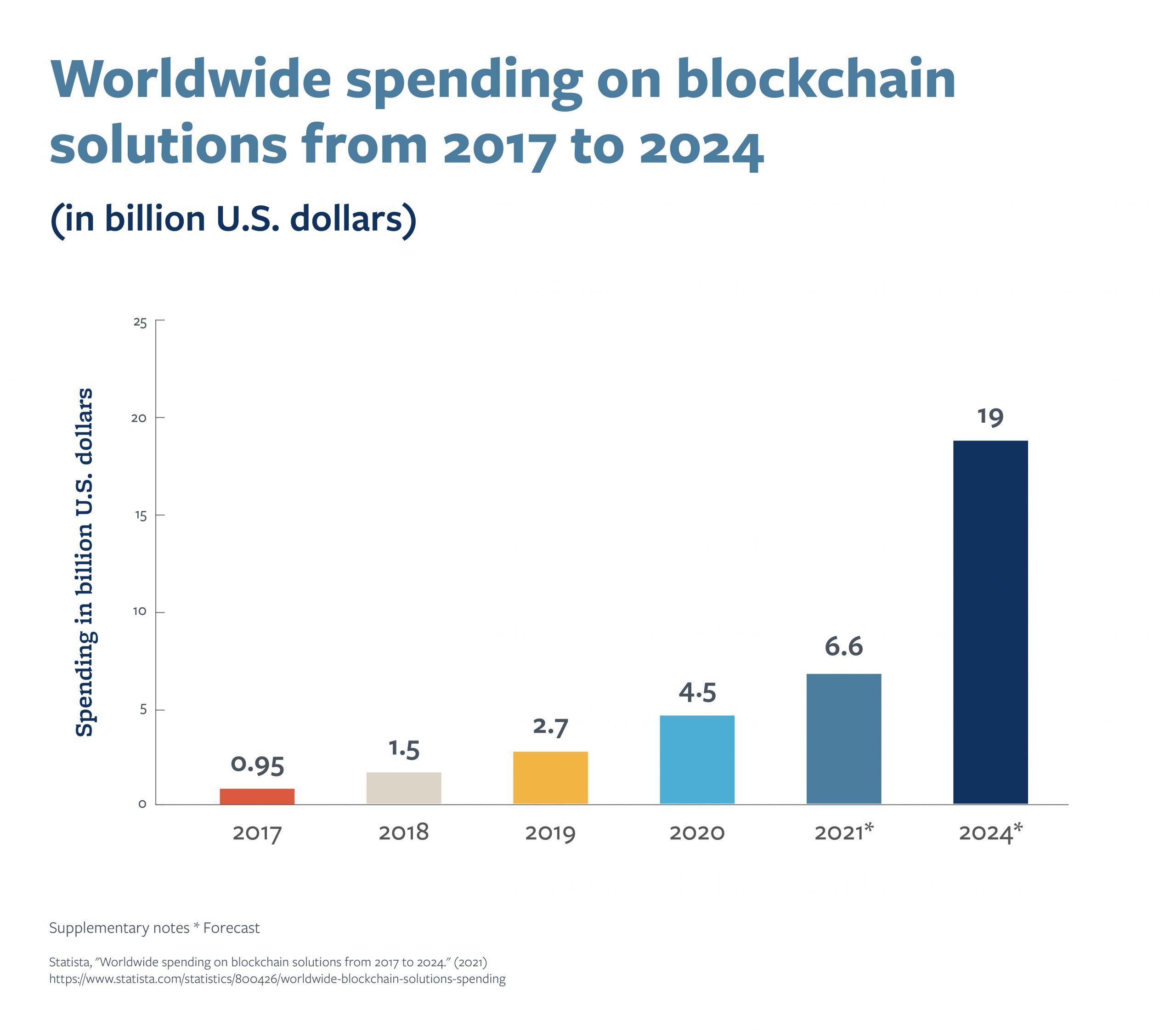
Blockchain is reinventing the way people and companies interact with each other, from how they trade goods, to how they transfer assets, to how they manage personal information. Blockchain can simplify and safeguard the ways we deliver healthcare, improve food safety and consume entertainment.
Still, many people have questions about this technology: How does blockchain work? Why is blockchain important? What can blockchain be used for?
We’ll explore those topics and address some blockchain use cases across industries such as finance, healthcare and entertainment. We’ll also discuss how to learn blockchain development. Everyone can grow from learning about the benefits of blockchain, particularly if they want to explore investing in cryptocurrency assets such as Bitcoin.
How Does Blockchain Work?
At its most basic, blockchain is a secure digital record of transactions, according to Deloitte. These records are distributed across a distributed database that is shared among the nodes of a computer network, ensuring transaction security and immutability.
Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger delineating who owns what and who transacts with whom. Each transaction is recorded as a self-contained piece (or “block”) of data that participants across the network can view but cannot alter. New transactions are recorded in separate blocks linked to the original in a “chain.” Hence, the name blockchain.
The underlying technology of blockchain is more complex, involving hashes, keys and rules established by network participants to authenticate the data. Blockchain transactions must be validated and the participants’ identities must be verified. This process builds a shared trust among network participants. According to the World Economic Forum, the blockchain ledger is “nearly impossible to cheat or hack” because of the verification process.
IBM offers an easy-to-understand guide on how blockchain works. Or, if you’re really interested in learning more and potentially transitioning into a fintech role, Berkeley FinTech Boot Camp teaches the in-demand skills you’ll need to transition into this exciting new field.
 Live Chat
Live Chat